- New Sailboats
- Sailboats 21-30ft
- Sailboats 31-35ft
- Sailboats 36-40ft
- Sailboats Over 40ft
- Sailboats Under 21feet
- used_sailboats
- Apps and Computer Programs
- Communications
- Fishfinders
- Handheld Electronics
- Plotters MFDS Rradar
- Wind, Speed & Depth Instruments
- Anchoring Mooring
- Running Rigging
- Sails Canvas
- Standing Rigging
- Diesel Engines
- Off Grid Energy
- Cleaning Waxing
- DIY Projects
- Repair, Tools & Materials
- Spare Parts
- Tools & Gadgets
- Cabin Comfort
- Ventilation
- Footwear Apparel
- Foul Weather Gear
- Mailport & PS Advisor
- Inside Practical Sailor Blog
- Activate My Web Access
- Reset Password
- Customer Service

- Free Newsletter


Tartan 37 Used Boat Review

C&C 33 Mark II Used Boat Review

Island Packet 350 Used Boat Review

Beneteau 393 Used Boat Review

How to Create a Bullet-Proof VHF/SSB Backup
Tips From A First “Sail” on the ICW

Tillerpilot Tips and Safety Cautions

Best Crimpers and Strippers for Fixing Marine Electrical Connectors

Are Wrinkles Killing Your Sail Shape?

Superlight Anchors: Not Just for Racers

Refining Furling Line Fairleads

Revive Your Mast Like a Pro
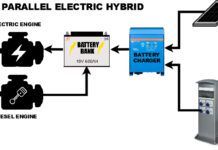
Diesel-Electric Hybrids Vs. Electric: Sailing’s Auxiliary Power Future

Sailing Triteia: Budget Bluewater Cruising

How To Keep Pipe Fittings Dry: Sealant and Teflon Tape Tests

How Much Does it Cost to Own a Sailboat in Quebec,…

Anode Basics: Dos and Don’ts

What’s The Best Bottom Paint?

Boat Hook and Fender Hacks


Product Hacks: Velcro, Bounce, Anti-Skid Mats and Pool Lights

Stopping Holding-tank Odors

Giving Bugs the Big Goodbye

Galley Gadgets for the Cruising Sailor

Cold Weather Clothes to Extend the Sailing Season

Five Best Gloves: Sailing and DIYing in All Weather

Sailing Gear for Kids

What’s the Best Sunscreen?

R. Tucker Thompson Tall Ship Youth Voyage

On Watch: This 60-Year-Old Hinckley Pilot 35 is Also a Working…

On Watch: America’s Cup

On Watch: All Eyes on Europe Sail Racing

Dear Readers
- Sailboat Reviews
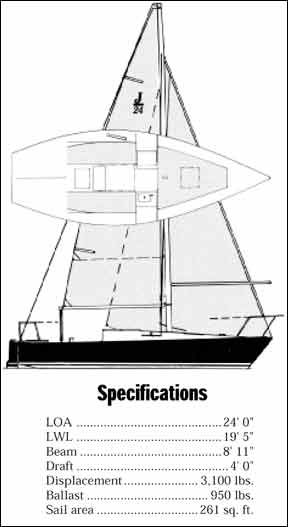
The right boat at the right time, the J/24 has proven to be a wildly successful one-design racer.

The J/24 is one of those boats that happened along at just the right time, with the right marketing to a ready market. Some may wonder whether the tale of her success would make a better textbook or a better storybook. Either way, much of the marine industry has studied her story, and then flattered her with the praise of emulation. However, no imitation or variation of the J/24 has yet to achieve her popularity.
Since her humble beginnings in 1976 in the garage of an amateur designer, thousands of boats have been sold from factories in Rhode Island, California, Australia, Japan, Italy, England, France, Brazil and Argentina. All of the builders are licensed by a company called J-Boats to build the J/24 to strict one-design tolerances. J-Boats is owned and run by two brothers—Bob and Rod Johnstone (the J in J-Boats).
Bob is the marketing whiz and Rod is the designer. Conservative estimates put their total revenue from the J/24, after buying the boats from the builders and selling them to the dealers, at several million dollars. Not bad considering how it all began….
Ragtime was a 24′ inspiration evolved by Rod Johnstone and his family in their garage as a two-year weekend project. Rod was a salesman for a marine publication, and an avid racer with a successful background in high-performance one designs. He had undertaken, but never completed, the Westlawn home-study course in naval architecture (although he has since been awarded an honorary degree so the school could use his name in its advertisements). Ragtime was launched in 1976, and was an instant winner, taking 17 firsts in 19 starts in eastern Connecticut. People began asking for their own boats.
At this time, brother Bob, also a respected racer, was working in the marketing department of AMF Alcort (Sunfish, Paceship, etc.). When Alcort declined to produce the J/24, Bob quit and formed JBoats. Tillotson-Pearson, builder of the Etchells 22 and the Freedom line of boats, was more receptive and production began in 1977. The first J/24s were as fast as Ragtime , and dominated regattas like the 1977 MORC Internationals. Bob made sure that the favorable results were well publicized; more than 200 boats were sold that year, and nearly 1,000 the next.
It was a big hit for a number of reasons. She moved into a void, appealing to two groups of sailors who were ripe for her type of racing: those who had outgrown athletic small boats, yet still yearned for the competition of one-design racing, and those who wished to compete without the expense, hassles and uncertainties of handicap racing.
The J/24 is a one design’s one design. Like the Laser, Windsurfer, and Hobie Cat, she is proprietary-built under the supervision of one company. Unlike most proprietary one designs, sails are not provided by the J/24’s builder. This was a particularly astute move by the Johnstones as it involved sailmakers in the class. Sailmakers comprise many of the big names in racing; by getting them in the regatta results, the Johnstones added instant credibility to the J/24’s budding status as a “hot” class. By the midwinter championship in 1979, almost every boat in the top 15 finishers had a sailmaker on board.
The big advantage that proprietary one designs have over “independent” one designs (classes with competing builders) is the power of centralized, bigbucks promotion. J-Boats has organized and promoted regattas, and had a heavy hand in running the class association. J/24s got a lot of press, thanks to JBoats. Full color, multi-page advertisements appeared monthly in the slick sailing magazines. Promotion has been primary; money is no object. J/24s have been donated for several high visibility USYRU championships. Big discounts have been given for fleet purchases (sometimes to effectively crush interest in competing one designs).
With the help of British enthusiasts, the Johnstones were able to make the J/24 an IYRU (International Yacht Racing Union) recognized class. More international lobbying got the J/24 into the Pan American Games.
There are some disadvantages to proprietary one designs. First, the class is in a real bind if the builder goes bankrupt. Likewise if the builder should ever abuse his power by ignoring class administration or changing construction of the boat to suit economic demands. Although a proprietary builder faces competition from other types of boats, there is no competition building his boat. This can inflate the price, especially when there are three substantial markups in the pricing structure (builder, J-Boats, and the dealer).
Construction
The J/24 has the distinct advantage of having been produced in great numbers and been subjected to the rigors of hard racing. It’s safe to say that nearly everything that could have broken, has broken, and that the J/24 is now almost bulletproof. J-Boats has done a commendable job in correcting nearly all of the “bugs” in the J/24. However, if you are planning to purchase a boat several years old you should be watchful for some of the old bugs.
Boats built during the first two years of production had particular problems with leaking along the hull-to-deck joint, delamination of the main bulkhead, and the attachment of the keel to the hull. The hull-to-deck leak was due to failure of the silicone sealant in the joint.
The inward-turning hull flange is overlapped by the deck, which is bedded in sealant and through-bolted at close intervals through a teak toe rail. Now this joint is bedded with 3M 5200, a pliable strong adhesive, and leaks are infrequent. Fortunately, the internal side of the joint is exposed throughout the boat’s interior, so recaulking is not difficult.
Harder to rectify is the problem of delamination of the main bulkhead. J/24s are raced hard, often with substantial rig tension. The chainplates pierce the deck and are bolted to the main bulkhead. The plywood bulkhead is tabbed with fiberglass to the hull and deck. The mast is stepped through the deck and sits on an aluminum beam, which is also tabbed to the main bulkhead. Rig tension pulls upward on the bulkhead while mast compression pushes downward on the beam, resulting in tremendous shearing forces on the bulkhead and its tabbing.
On some of the older J/24s, the plywood has delaminated, letting the mast “sink” 1/4 inch or more. Owners of these boats have either returned them to the factory for replacement of the bulkhead, or ground off the delamination and reglassed the bulkhead themselves. The builder now uses a better grade of plywood and installs screws to reinforce the bulkhead tabbing. As an added precaution, the boat owner may wish to bolt the mast-bearing beam to the bulkhead with an angle-iron.
The third problem with some of the older J/24s is the keel-to-hull attachment. The builder used to fill the keel sump with a vermiculite mixture of resin and plant fiber. The keel bolts were fastened through the vermiculite which, when saturated with water, is less rigid than solid laminations of fiberglass. After several years of sailing, or a hard grounding, the keel bolts would begin to work, and the keel would loosen enough to be able to be wobbled by hand with the boat suspended from a hoist. The first sign of this problem is the appearance of a crack along the keel stub. Tightening of the keel bolts, which are quality stainless steel, is a simple but temporary fix. What is needed is a backing plate for the bolts, bedded on top of the vermiculite.
There was a variety of other problems with early J/24s: The mast has three internal halyards; two jib halyards exit below the headstay with the spinnaker halyard above. On the older boats, a large square hole was cut in the mast to accommodate the sheaves, leaving an open, poorly supported space adjacent to the spinnaker sheave. This is sometimes the source of mast cracks; the fix is to weld a plate over it.
In January of 1980, the J/24 got much-improved companionway and forward hatches. The hatches on older boats were molded of thin fiberglass, and had a tendency to leak and fracture under the weight of heavy crew members. The new forward hatches are lexan, and the companionway hatch is now much heavier with a lower profile.
The J/24’s rudder is heavy and strong. The builder claims you can hang a 900 pound keel from the rudder tip without breaking it. Although the J/24’s rudder pintles appear more than adequate, after several years of use they have been known to develop corrosion cracks where the pintle is welded to its strap. In 1981, the builder began equipping J/24s with weldless pintles; the builder also offers the new system as a replacement for old boats.
The starboard chainplate bolts through both the bulkhead and the hull liner. The port chainplate bolts through only the bulkhead. After the first two years of production, the port bulkhead was reinforced with fiberglass in the chainplate area. On earlier boats, a backing plate should be added to prevent the chainplate bolts from elongating their holes.
The hull and deck of the J/24 are cored with balsa, which makes them stiff, light, quiet and relatively condensation-free. We have heard of occasional delaminations resulting from trailering with improperly adjusted poppets. The Kenyon mast section is the same as that used on the Etchells 22, a bigger boat. It is more than adequate for any strength of wind.
The J/24 does not have positive flotation, and she has been known to capsize in severe conditions. This is usually not a problem as she floats on her side with the companionway well out of the water. However, should the leeward cockpit locker fall open, water can rush below, filling the cabin and causing her to sink. While fastening the lockers in heavy weather prevents the problem, the manufacturer began to seal off the lockers from the cabin with an additional bulkhead several years ago, as a safety measure.
Of the 2,500 J/24s sold in the US, nearly 2,000 of them have been built by Tillotson-Pearson in Rhode Island. The others were built by Performance Sailcraft in San Francisco, which is now defunct. New boats are now shipped cross country. Top west coast sailors tell us they favor the east coast built boats, claiming the keels and rudders on the west coast built boats are too thick to be competitive. The west coast keels are thick because they are covered with injection-molded gelcoat. Tillotson-Pearson fairs the keels with auto body putty.
Handling Under Sail
The J/24’s PHRF rating ranges from 165 to 174, depending on the handicapper. She rates as fast as or faster than a C&C 30, Santana 30, or Pearson 30. One must remember that, because the J/24 has attracted competent owners, her PHRF rating is probably somewhat inflated. While the J/24 is an excellent training boat because she is so responsive, a beginning racer may have an especially hard time making her perform to her PHRF rating.
Aside from her speed, the J/24’s greatest asset is her maneuverability. With her stern hung rudder she can be turned in her own length, sculled out to a mooring in light air, and brought to a screeching halt by jamming the rudder over 90 degrees.
The J/24 has a narrow “groove;” it takes a lot of concentration to keep her going at top speed. She is sensitive to backstay trim, sheet tension, weight placement and lower shroud tension. The lower shrouds act like running backstays, because they are anchored aft of the mast. They must be loosened in light air to create some headstay sag, and then tightened in heavy air to straighten the mast, making backstay tension more effective in removing the sag.
Sheet tension is also critical. Top crews rarely cleat the genoa sheets, having one crewmember hold the tail while hiking from the rail. Some of the best sailors even lead the jib to the weather winch so the sail can be trimmed without sending crew weight to leeward.
The class rules allow you to race with a mainsail, a 150% genoa, a working jib and a single spinnaker. This makes sail selection simple and the inventory affordable (about $2,600 total). However, the one genoa must carry the boat all the way from a flat calm up to 20 knots or more. To be competitive in light air, the genoa must be full; yet to hold the boat level with this full genoa in a strong breeze, you need a lot of crew weight. Most of the top crews are now sailing with five people on board for a total crew weight of 800 to 900 pounds. The J/24 is a small boat, and the additional fifth crew member really makes the boat cramped. Add to this the increasing trend of some skippers making the crew sit in the cabin on the leeward bunk in light air, and you have a boat which can be less than fun to crew on.
There are two worthwhile improvements that can help a J/24’s performance. To decrease the boat’s slight tendency toward a lee helm in light air, the mast should be cut to minimum length allowed in the class rules, and the headstay should be lengthened to the maximum allowed to give the mast more rake. The other improvement is fairing the keel to minimum dimensions. The keel is much thicker than is necessary for optimum performance. It comes relatively fair from the builder, but most owners will want to grind off the builder’s auto-body filler and sharpen the trailing edge. On some of the older boats, the trailing edge is twice the minimum thickness.
Some racers go so far as to spend $500-$1,000 to have the keel professionally faired.
While all indications are that the builder has excellent quality control, there have been complaints that some of the spars provided by Kenyon in the last two years have come with the wrong length shrouds, or widely differing bend characteristics. One top sailor said he would never buy a used J/24 without first making sure that he could make the mast stand straight sideways with substantial shroud tension.
The J/24 is best suited for racing; there are many boats in her size range that are far more comfortable and practical for daysaiIing. However, the J/24 is a joy to sail under mainsail alone. Unlike most boats, she balances and sails upwind at a respectable speed, and her maneuverability gives her tremendous freedom in crowded harbors.
Handling Under Power
The J/24 is powered by an outboard engine; an inboard is not feasible or available. Class rules require that an outboard with a minimum of 3.5 hp be carried while racing. Most owners opt for a 3.5-4 hp outboard. It provides adequate power and is as much weight as you want to be hefting over a transom. Although the cockpit locker is plenty big enough, most owners stow the outboard under a berth in the cabin to keep the weight out of the stern. This makes using the outboard inconvenient. The factory-supplied optional outboard bracket has a spring-loaded hinge to lift the engine for easy mounting; we recommend it. Because the outboard is likely to be stored in the cabin, a remote gas tank will keep fuel spillage and odor to a minimum.
Above Decks
The J/24 is very well laid out, yet she is still not a comfortable or easy boat to crew on. When she was first launched, sailors said her layout could be no better, and she was copied by manufacturers of competing boats. However, after years of racing, sailors have discovered several things that could be improved.
Cockpit winches are located just forward of the mainsheet traveler, which spans the middle of the cockpit. Many sailors have moved the winches forward, so the crewmember tacking the genoa can face forward instead of aft during a tack. It pays to check to see if relocated deck hardware was installed properly; one J/24 owner we know discovered that the previous owner had moved the winches, but hadn’t installed proper backing plates or filled the original holes correctly. As a result, seepage had occurred and several square feet of the balsa-cored deck above the quarterberth had become sodden and rotten.
The standard mainsheet cleat is attached to the traveler car so that, when you trim the sheet, you inadvertently pull the car to weather. Many sailors have solved this by mounting a fixed cleat with a swivel base at the center of the traveler bar.
On older boats the backstay was single-ended at the transom. Boats now come with a double-ended backstay led forward to the helmsman on each side of the cockpit. Foot blocks need to be mounted on the traveler to keep helmsmen from falling to leeward as the boat heels (you must steer from forward and well outboard of the traveler).
For those who plan to try cross-sheeting to the weather winch, leading the jib sheets through Harken ratchet blocks is advised. Most sailors will also want to mount barber haulers to pull the genoa sheet outboard in strong winds. Cam cleats for the barber haulers should be mounted on the companionway so they “self-cleat” when led to the weather winch.
Cabin-top winches for the halyards and spinnaker guys are optional and essential. Because the J/24 has single spinnaker sheets, most sailors mount “twings,” which pull the guy down to the deck outboard of the shrouds when reaching.
In the search for a cleaner deck, it is now common to mount the spinnaker halyard cleat on the mast. Most sailors use only one jib halyard. Although a second jib halyard is optional, it is necessary only for long distance handicap racing. On short one design courses it is better to struggle along overpowered than to place crew weight on the bow to change headsails. Instruments are also unnecessary in one design racing. There are more than enough boats on a one design race course to judge your speed without the help of a speedometer.
The J/24 comes equipped with a Headfoil II grooved headstay system, which works very smoothly. Early boats came with Stern Twinstays, which have occasionally failed when the bearings freeze up with age. Some sailors have exchanged the grooved headstay system for cloth snaps on their headsails (you seldom change sails anyway). We applaud this idea, as it makes the sails more manageable in severe weather.
Although the flat decks are well suited for racing, the cockpit is less than comfortable for daysailing. There are no seat backs and the boom is dangerously low. Visibility with the deck-sweeping 150% genoa is terrible, and is often the cause of nightmarish collisions on crowded race courses. Lower life lines are optional and recommended for those with children, but they interfere with fast tacks when racing. The boom is rigged with a 4-to-1 vang, which is swiveled on the more recent J/24s to be adjustable from either rail on a windy spinnaker reach. The boom is also rigged with reef lines which exit through stoppers at the gooseneck.
Top sailors have discovered that the boat always sails better without a reef, which is a good thing, because the stoppers are both difficult to operate and have a history of slipping.
The interior is simple and functional. On most boats it is used for little more than sail storage. However, for a couple who enjoys roughing it, it could make for occasional weekend cruising. The first thing you notic below is the lack of headroom. You can sit in comfort, but to move about you must crawl.
The interior is finished off in bare white gelcoat. Early boats had coarse, non-skid gelcoat on the overhead. While this may have been more attractive than smooth gelcoat, it really did a number on elbows and bald heads. It also tended to collect dirt and mildew. Earlier through-bolted deck fittings were capped with acorn nuts. Now the nuts lie flush with the overhead—less pain when bumped.
A molded hull liner is used to form the two quarter berths, the cabin sole, and two lockers and a galley just aft of the main bulkhead. One locker is deep enough to serve as a wet locker for foul weather gear; the other is best used to store the rudiments of a meal. The galley consists of a sink with a hand pump. A small, two burner stove could be mounted in the small, removable “table” forward of the port quarter berth. The icebox, a large portable cooler made by Igloo, has a piece of teak glued to it and doubles as a companionway step. After a season or two of jumping on the ice chest, the lid disintegrates.
The forward V-berth, although divided by the mast, is still large and comfortable enough for a couple. The boat does not come equipped with a head. To avoid the extra drag of a through-hull fitting, portable heads are often used. We would rather use a cedar bucket—there simply isn’t enough space in the cabin of a J/24 to cohabitate with a portable head. If you plan to seriously race, you won’t want to load the boat’s lockers with cruising equipment. If you do cruise, it will probably be out of a duffel bag.
J/24: How Trailerable?
The J/24 is not launchable from a boat ramp, unless the ramp is steep, paved or of hard sand, and you use a long extender between the tongue of the trailer and your trailer hitch. Her 3,100 pounds (fully loaded) require a big, 8-cylinder vehicle to tow her. She is easily launched from a 2-ton hoist which can attach to a strap on her keel bolts. However, the hatch slides just far enough forward to allow the hoisting cable to clear it, so the hatch tends to get chewed by the cable.
The J/24 was originally designed to sail at a displacement of 2,800 pounds. The class minimum was later increased to 3,100. The original single axle trailer provide as a factory option was barely adequate for the intended, 2,800 pound boat, and totally inadequate for a fully loaded boat. Tales abound of blown tires and broken trailer welds. The factory now offers both a single and double axle trailer; we recommend the double axle.
If you want to seriously race a J/24, trailering is a necessity. Local fleets grow and shrink each year with the whims of their members, but national and regional regattas continue to attract many participants. Make no mistake, however; trailering is expensive.
The owning and maintenance of a big car, the gas and tolls of trailering, and the housing of crew are not cheap.
Conclusions
The appeal of the J/24 is as a racer. If you plan to do anything else, she is not for you. Although the J/24 is relatively easy to sail, she is very difficult to sail well. To many people, she represents a chance to compete in the big leagues; by traveling to major regattas you can sail against some of the best sailors in the country. However, the big leagues are tough—if you like to race with a pick-up crew and a hangover you’d also better be satisfied with finishing last.
One appeal of the J/24 is that, unlike many big league boats, you can always come home and sail because the boat has so big a following. There are enough boats to race it one-design almost anywhere; and in a pinch, there is always handicap racing. As long as you don’t want to travel, the boat is inexpensive to maintain.
Despite our effort to highlight every flaw that has appeared throughout the J/24’s evolution, we’d like to emphasize that she is more hardy than most boats of her type. Few boats can take the punishment that a J/24 gets during a season of racing and come through with so few scars. No racing boat will appreciate; but the J/24 can keep her value.
The dream boat with the fairy tale success story has turned out, after all, to be a rugged winner in the real world.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Log in to leave a comment
Latest Videos

J Boats J/9 Sailboat Review and Boat Tour

3 Tips for a Dry Boat – DIY Boat Maintenance 101

Jeanneau’s New Rule Breaking Sailboat – Sun Odyssey 350 Boat Review

A Fiberglass Cleaning Boat Hack You Have To Try!
Latest sailboat review.

- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information
- Online Account Activation
- Privacy Manager

IMAGES
VIDEO